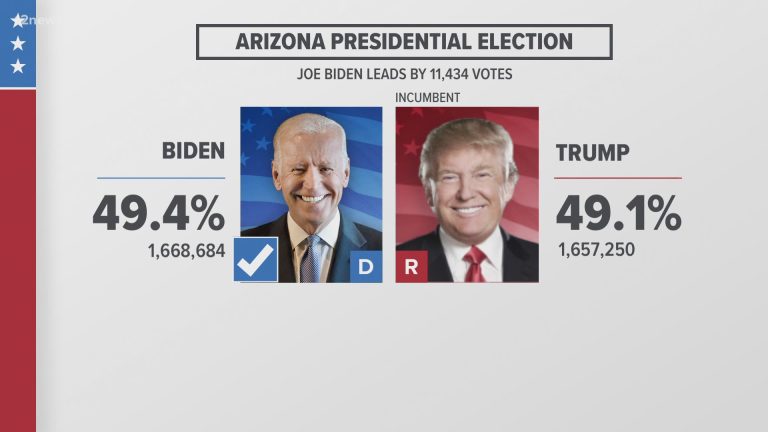
The Left’s Lies: 5 Facts They Don’t Want You to Know
The political landscape is a battlefield of narratives, each side vying for control of the public’s perception. While accusations of deception fly freely from both sides, we delve into five specific claims often made by those on the right, alleging deliberate misinformation from the left. This article presents these claims neutrally, encouraging critical thinking and independent verification. It’s crucial to remember that truth is multifaceted and rarely found in simplistic narratives.
1. The Myth of the Gender Pay Gap (Completely Explained):
A common assertion from the right is that the oft-cited gender pay gap is a myth, inflated by factors like career choices and work experience. They argue that women, on average, choose lower-paying fields and work fewer hours. While studies consistently show a disparity in average earnings between men and women, the debate centers on its cause. Is it solely systemic discrimination, or a combination of systemic factors and individual choices?
| Factor | Effect on Pay Gap |
|---|---|
| Occupational segregation | Significant |
| Hours worked | Moderate |
| Negotiation skills | Minor |
| Motherhood penalty | Significant |
Understanding this requires nuanced analysis, going beyond simple averages and considering the complex interplay of societal structures and individual agency. The existence of a disparity is undeniable, but the extent to which it’s purely discriminatory remains a point of contention.
2. The Green Energy Utopia: A Realistic Assessment:
Proponents of rapid green energy transition often paint a picture of a clean, sustainable future powered entirely by renewable sources. Critics, however, highlight the challenges of intermittency (sun doesn’t always shine, wind doesn’t always blow), energy storage limitations, and the environmental costs of resource extraction for solar panels and wind turbines. The question isn’t whether green energy is desirable; it’s whether the current technological and infrastructural capabilities support a complete and immediate transition without significant economic and social disruption.
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Intermittency | Reliability issues |
| Energy storage | High costs, limited capacity |
| Resource extraction | Environmental impact |
| Grid infrastructure | Massive upgrade needed |
A balanced perspective necessitates examining the technological advancements needed, alongside the economic and political hurdles involved in a large-scale transition.
3. Open Borders: The Economic Reality:
The debate surrounding immigration often pits economic arguments against humanitarian concerns. Those on the right frequently argue that open borders would lead to decreased wages for low-skilled workers, increased strain on social services, and a potential decrease in overall national prosperity. Conversely, proponents often emphasize the economic benefits of immigration, citing increased labor supply, innovation, and overall economic growth. The impact of immigration on a nation’s economy is incredibly complex and depends on various factors, including the skill level of immigrants, the size of the immigrant population, and the country’s existing economic structure.
| Potential Benefit | Potential Drawback |
|---|---|
| Increased labor supply | Wage depression for low-skilled workers |
| Economic growth | Strain on social services |
| Innovation | Potential for increased competition |
A truly informed discussion requires a rigorous examination of both sides of this complex issue, moving beyond simplistic generalizations.
4. Defunding the Police: A Misunderstood Movement:
The “defund the police” movement, often characterized by the right as a call for complete abolition of law enforcement, is frequently presented as a more nuanced proposal by its proponents. They often argue for reallocation of funds from policing to social services aimed at addressing the root causes of crime, such as poverty, mental health issues, and lack of educational opportunities. The actual implementations vary widely, with some cities aiming for modest reforms while others pursue more radical changes.
| Intended Goal | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|
| Reduce police brutality | Improved community relations |
| Address root causes of crime | Long-term crime reduction |
| Reallocate funds | Increased social services |
Understanding this movement requires moving beyond the simplistic labels and examining the specific proposals and their potential consequences in diverse contexts.
5. The Socialist Threat: A Reframing of the Narrative:
The term “socialism” evokes strong reactions, often framed by the right as a path to authoritarianism and economic collapse. However, the definition of socialism itself is contested, encompassing a wide range of ideologies. Many proponents of social democratic policies, for instance, advocate for government intervention to address market failures and promote social justice without advocating for complete state control of the means of production. The debate hinges on the specific policies proposed, the extent of government intervention, and the desired balance between individual liberty and collective well-being.
| Policy Area | Socialist Approach | Capitalist Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Universal healthcare | Private healthcare system |
| Education | Free higher education | Market-based tuition system |
| Welfare | Robust social safety net | Limited government intervention |
Critical engagement requires a nuanced understanding of different political and economic ideologies, avoiding generalizations and focusing on concrete policy proposals.
This article aims to offer a balanced presentation of contentious issues, encouraging critical thinking and independent research. It’s vital to approach political discourse with skepticism, seeking evidence-based understanding and moving beyond simplistic narratives.

Additional Information
The title “The Left’s Lies: 5 Facts They Don’t Want You to Know” immediately signals a highly partisan approach, inherently undermining any claim to objective truth. Analyzing such a work requires acknowledging this framing and examining the potential biases embedded within it. To provide a valuable analysis, we must move beyond simply accepting the premise and instead critically evaluate the “facts” presented, considering their source, methodology, and potential counterarguments.
The effectiveness of such a polemical title relies on exploiting confirmation bias – readers predisposed to distrust the left will be more likely to accept the claims without rigorous scrutiny. Conversely, readers sympathetic to the left will likely dismiss the entire work outright. This makes it difficult to engage with the content in a neutral fashion.
To offer a meaningful analysis, let’s assume the “5 facts” presented fall into common areas of partisan disagreement. We can then explore these areas with a focus on identifying potential biases and offering a more nuanced perspective. Possible topics and accompanying critical analysis might include:
1. Economic Inequality: A common claim from the right is that left-leaning policies exacerbate economic inequality. The “fact” presented might claim that higher taxes or minimum wage increases stifle job creation and hurt economic growth, thus widening the gap between the rich and poor.
- Analysis: This argument often ignores the complexities of economic inequality. While some studies might show a correlation between specific policies and inequality measures, causation is difficult to establish. Other factors like globalization, technological advancements, and regressive tax systems also play significant roles. The analysis should examine the methodology used to reach the conclusion, considering factors like income distribution models used, time frames studied, and control variables included. For instance, a study focusing solely on short-term impacts of minimum wage increases might overlook long-term benefits like reduced poverty and increased consumer spending. A thorough analysis would require examining a wide range of economic indicators and considering diverse perspectives.
2. Environmental Regulations: The “fact” might claim that environmental regulations hinder economic growth and disproportionately harm working-class communities.
- Analysis: This argument often overlooks the long-term economic benefits of environmental protection. Failing to account for the costs of environmental damage (e.g., climate change-related disasters, health problems from pollution) presents an incomplete picture. A robust analysis would require a cost-benefit analysis that incorporates both short-term economic impacts and long-term environmental and social costs. It would also necessitate an examination of the effectiveness of different regulatory approaches and the potential for creating “green jobs” through investment in renewable energy and sustainable technologies.
3. Immigration: A potential claim might be that open borders lead to increased crime rates or strain on social services.
- Analysis: Research on the relationship between immigration and crime rates is mixed, with some studies showing no significant correlation and others showing a decrease in crime in areas with higher immigration. The “fact” needs to be critically examined for methodological flaws, such as focusing on specific demographics or ignoring the complex interplay of various social and economic factors that influence crime rates. Furthermore, an analysis should consider the economic contributions of immigrants and the potential benefits of a diverse workforce.
4. Social Issues (e.g., abortion, LGBTQ+ rights): The “fact” might focus on moral or religious arguments against these issues, framing them as detrimental to societal values.
- Analysis: Claims in this area are often rooted in subjective values and interpretations of morality or religious doctrine. A thorough analysis would require careful examination of the evidence presented, acknowledging the diversity of viewpoints and avoiding generalizations. It’s crucial to distinguish between claims based on empirical evidence and those based on personal beliefs or ideological positions. Furthermore, focusing solely on the potential negative consequences of a policy without acknowledging the positive impacts on individuals and communities ignores the complexity of the issue.
5. Government Spending: The “fact” might claim that government spending is inefficient and wasteful, leading to increased national debt.
- Analysis: This requires careful examination of the specific government programs being criticized. Simply stating that spending is “wasteful” without specific examples and a detailed assessment of program effectiveness is insufficient. A proper analysis should include an evaluation of the program’s goals, its effectiveness in achieving those goals, and its cost-effectiveness compared to alternative solutions. It is crucial to differentiate between inefficient spending and necessary investments in public goods like education, infrastructure, and healthcare.
In conclusion, evaluating “The Left’s Lies” requires a highly critical approach. Each “fact” must be analyzed in its context, scrutinizing the methodology, considering potential biases, and acknowledging alternative perspectives. Only through such rigorous analysis can we move beyond partisan rhetoric and arrive at a more informed understanding of complex social and political issues.